Contents
To use sudo when using the command line, simply type “sudo” before the command you wish to run. Sudo will then prompt you for your password. Sudo will remember your password for a set amount of time (15 minutes by default)..
How do I sudo as root user?
Open a terminal Window/App. Press Ctrl + Alt + T to open the terminal on Ubuntu. When promoted provide your own password. After successful login, the $ prompt would change to # to indicate that you logged in as root user on Ubuntu.
How do I sudo in Ubuntu?
This command will give you superuser access with root’s environment variables.
- Enter the command sudo passwd root . This will create a password for root, essentially “enabling” the account.
- Type sudo -i . Enter the root password when prompted.
- The prompt will change from $ to # , indicating you have root access.
What is a sudo user in Linux?
sudo , which is an acronym for superuser do or substitute user do, is a command that runs an elevated prompt without a need to change your identity. Depending on your settings in the /etc/sudoers file, you can issue single commands as root or as another user.
Is a sudo user a root user?
What is Sudo? The sudo (superuser do) command is a command-line utility that allows a user to execute commands as the root or a different user. It provides an efficient way to grant certain users the appropriate permissions to use specific system commands or run scripts as the root user.
What is the sudo command?
The sudo command allows you to run programs with the security privileges of another user (by default, as the superuser). It prompts you for your personal password and confirms your request to execute a command by checking a file, called sudoers , which the system administrator configures.
How do I give root permission to a folder in Linux?
To change directory permissions in Linux, use the following:
- chmod +rwx filename to add permissions.
- chmod -rwx directoryname to remove permissions.
- chmod +x filename to allow executable permissions.
- chmod -wx filename to take out write and executable permissions.
How do I give root permission to user in Redhat Linux?
To enable sudo for your user ID on RHEL, add your user ID to the wheel group:
- Become root by running su.
- Run usermod -aG wheel your_user_id.
- Log out and back in again.
What is GID and UID? Unix-like operating systems identify a user by a value called a user identifier, often abbreviated to user ID or UID. The UID, along with the group identifier (GID) and other access control criteria, is used to determine which system resources a user can access.
Is sudo same as root?
Executive summary: “root” is the actual name of the administrator account. “sudo” is a command which allows ordinary users to perform administrative tasks. “Sudo” is not a user.
What can I use instead of sudo?
Commercial Alternatives
- Core Privileged Access Manager (BoKS)
- CyberArk On-Demand Privileges Manager.
- Centrify DirectAuthorize includes a dzdo command that functions similarly to sudo. They also include a sudo migration tool.
How do I enable root access in Linux?
Enable or disable remote root login
- To enable remote root login, enter the following command: /etc/ssh/sshd_config: PermitRootLogin yes #enabled.
- To disable remote root login, enter the following command: /etc/ssh/sshd_config: PermitRootLogin no #disabled.
What is the user ID of root in Linux?
The root account is the special user in the /etc/passwd file with the user ID (UID) of 0 and is commonly given the user name, root. It is not the user name that makes the root account so special, but the UID value of 0 . This means that any user that has a UID of 0 also has the same privileges as the root user.
Why is sudo command used in Linux?
The sudo command allows you to run programs with the security privileges of another user (by default, as the superuser). It prompts you for your personal password and confirms your request to execute a command by checking a file, called sudoers , which the system administrator configures.
How do I get root permission in Linux? How to get root access on Linux operating system?
- Please click on the lower left corner of the icon (start button).
- Click Terminal menu item to open the terminal.
- Input the command below: % sudo su –
- Press Enter.
- Your terminal prompt will become #.
- You now have root privleges on all operations in the terminal window.
How do I give a regular user root privileges using sudo in Linux Unix? How to Give Root Privileges to a User in Linux
- Method 1: Adding to Root Group using usermod. Let see how we can grant normal user root access by adding to root group.
- Method 2: Adding to Root Group using Useradd Command.
- Method 3: Editing /etc/passwd file.
- Method 4: Setting as Sudo User.
How do I login as root in Linux terminal?
Switching to the root user on my Linux server
- Enable root/admin access for your server.
- Connect via SSH to your server and run this command: sudo su –
- Enter your server password. You should now have root access.
How do I give root permission to user in Ubuntu?
How To Add a User and Grant Root Privileges on Ubuntu 18.04
- Step 1: Add the Username. In my example, I’ll be adding my cat’s name, Tom, using the adduser command.
- Step 2: Grant Root Privileges to the User. visudo.
- Step 3: Verify User Has Privileges.
What is sudo in Linux?
sudo , which is an acronym for superuser do or substitute user do, is a command that runs an elevated prompt without a need to change your identity. Depending on your settings in the /etc/sudoers file, you can issue single commands as root or as another user.
How install sudo Linux?
At first, login to an user account and open a terminal to execute the following commands:
- Start becoming superuser with su .
- Now, install sudo with apt-get install sudo .
- Add the user account to the group sudo with /sbin/adduser username sudo .
- Now, log out and then log in with the same user.
Can all users use sudo?
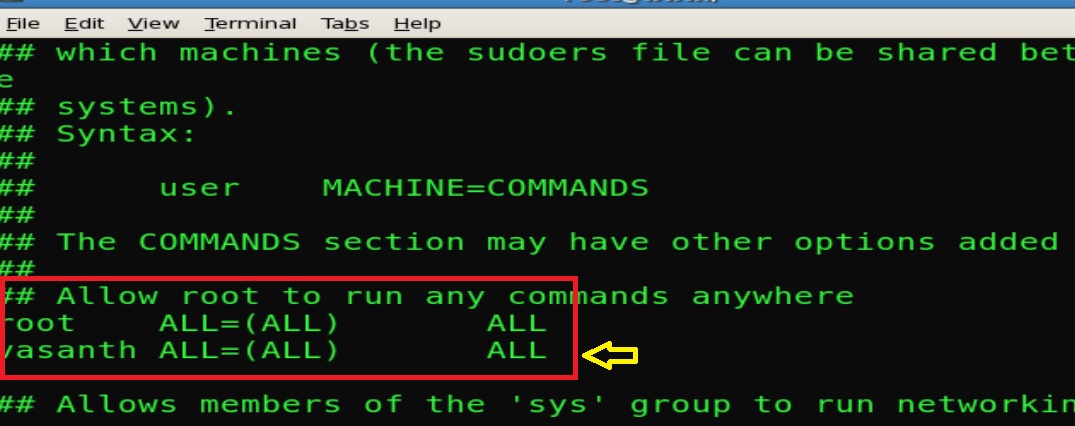
To add users to the list of people who can use sudo , you need to edit the sudoers file. It is vitally important that you only ever do so using the visudo command. The visudo command prevents multiple people from trying to edit the sudoers file at once.
Is sudo password same as root?
Password. The primary difference between the two is the password they require: while ‘sudo’ requires current user’s password, ‘su’ requires you to enter the root user password.
Can any user use sudo?
Only people in /etc/sudoers can use sudo, and ideally very very few people (like, one) should have such access in a shard system. You may configure /etc/sudoers to permit any user inside the sudoers group.
Why do I need to use sudo? Sudo (superuser do) is a utility for UNIX- and Linux-based systems that provides an efficient way to give specific users permission to use specific system commands at the root (most powerful) level of the system. Sudo also logs all commands and arguments.